|
| What is AIS?
AIS = Automatic Identification System
A quick look at the basic technology
Summary:
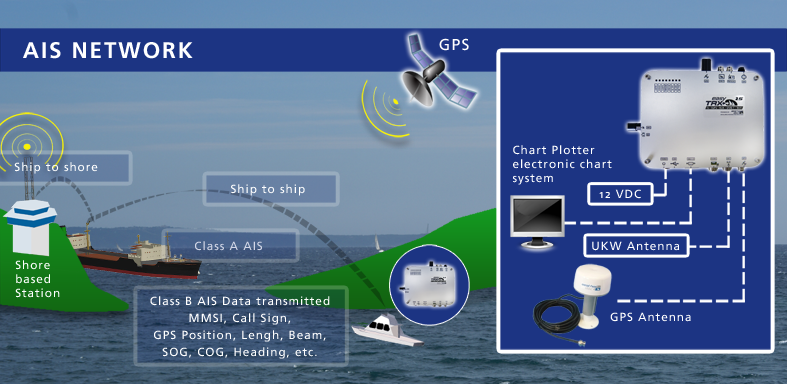
The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a maritime transponder/receiver system defined by the IMO (international maritime organization) AIS operates in the VHF frequency band. AIS main objectives are :
- to improve maritime safety
- to protect the maritime environment
Practically the AIS:
- assists collision avoidance (AIS ship-to-ship)
- enables ports and coastal states to identify ships and to manage and supervise the traffic in their waters (AIS Coast station).
Description:
AIS is a system used by ships and vessels for identification at sea. It helps to resolve the difficulty of identifying ships when not in sight (e.g. at night, in radar blind arcs or shadows or at distance) by providing ID, position, course, speed and other ship data with all other nearby ships and VTS stations. The IMO SOLAS requires AIS to be fitted aboard all ships of gross tonnage >= 300 for international voyages. The ship data is displayed on a AIS data capable chartplotter with an ship symbol or even on AIS data capable navigation software.
The AIS also receives heading information from the ship’s compass and transmits this at the same time. Other information, such as the vessel name and VHF call sign, is entered when installing the equipment and is transmitted less frequently. The signals are received by AIS transponders fitted on other ships or on land based systems, such as VTS systems.
In order to ensure that the VHF transmissions of different AIS transponders do not occur at the same time they are time multiplexed. In order to make the most efficient use of the bandwidth available, vessels which are anchored or are moving slowly transmit less frequently than those that are moving faster or are maneuvering. The update rate of fast maneuvering vessels is similar to that of a conventional marine radar.
- MMSI number of vessel – vessel’s unique identification
- Navigation status – “at anchor”, “under way using engine” or “not under command”
- Rate of turn – right or left, 0 to 720 degrees per minute
- Speed over ground – 0.1 knot resolution from 0 to 102 knots
- Position accuracy
- Longitude – to 1/10000 minute and Latitude – to 1/10000 minute
- Course over ground – relative to true north to 0.1 degree
- True Heading – 0 to 359 degrees from eg. gyro compass
- Time stamp – UTC time accurate to nearest second when this data was generated
Not all of above data is displayed (Quantity of shown data is software of the Chartplotter).
- MMSI number of vessel – vessel’s unique identification
- Speed over ground – 0.1 knot resolution from 0 to 102 knots
- Course over ground – relative to true north to 0.1 degree
In addition, the following data is broadcast every 6 minutes:
- MMSI number – vessel’s unique identification
- IMO number
- Radio call sign – international radio call sign assigned to vessel
- Name – Name of vessel, max 20 characters
- Type of ship/cargo
- Dimensions of ship – to nearest meter
- Location of positioning system’s (eg. GPS) antenna onboard the vessel
- Draught of ship – 0.1 meter to 25.5 meters
- Destination – max 20 characters
- ETA (estimated time of arrival) at destination – UTC month/date hour:minute
Above given information is not complete and should give only an overview about the AIS topic. For more details please have a look to the following links :
US Coust Guardwww.imo.orgwww.aislive.com